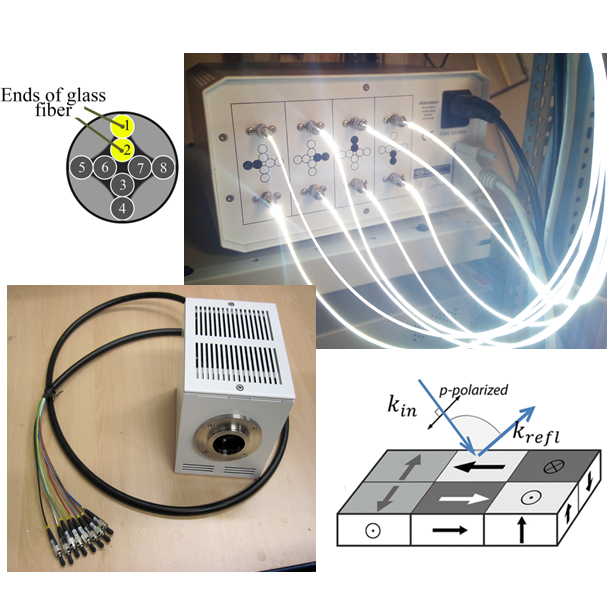
Selective sensitivity in Kerr microscopy
I. V. Soldatov and R. Schäfer, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88, 073701 (2017)
A new technique for contrast separation in wide-field magneto-optical Kerr microscopy is introduced. Domain images with orthogonal in-plane sensitivity are displayed simultaneously at real-time, and images with pure in-plane or polar contrast are obtained.
.
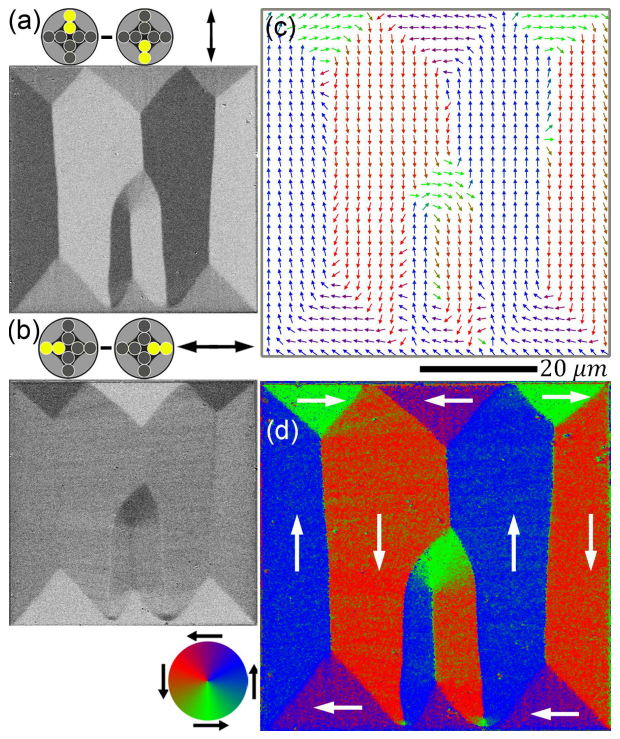
Advances in quantitative Kerr microscopy
I. V. Soldatov and R. Schäfer, Phys. Rev. B 95, 014426 (2017)
An advanced wide-field Kerr microscopy approach to the vector imaging of magnetic domains is demonstrated. The method is applied to the investigation of the magnetization process in a patterned Permalloy film element and GaMnAs semiconducting film.
.
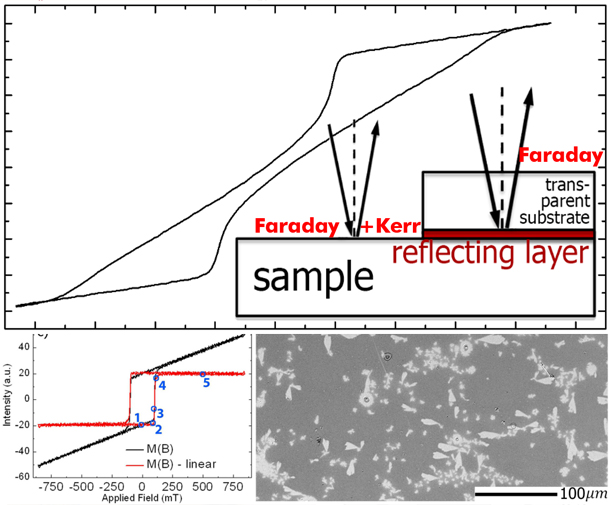
Advanced MOKE magnetometry in wide-field Kerr-microscopy
I. V. Soldatov and R. Schäfer, J. Appl. Phys. 122, 153906 (2017)
In this paper, an advanced experimental method, based on a motorized analyzer, is introduced which allows to compensate the Faraday contributions, thus leading to pure MOKE (Magneto-Optical Kerr Effect) loops. A wide field Kerr microscope, equipped with this technology, works well as a laser-based MOKE magnetometer, additionally offering domain images and thus providing the basis for loop interpretation.
.

Size analysis of sub-resolution objects by Kerr microscopy
I. Soldatov, W. Jiang, S.G.E. Te Velthuis, A. Hoffmann and R. Schäfer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 (26), 262404 (2018)
A Kerr microscopy method for the quantitative measurement of the size of magnetic objects that are smaller than the resolution limit is proposed. It can be applied to domain walls, bubble domains and magnetic skyrmion-bubble hybrid microstructures.
.
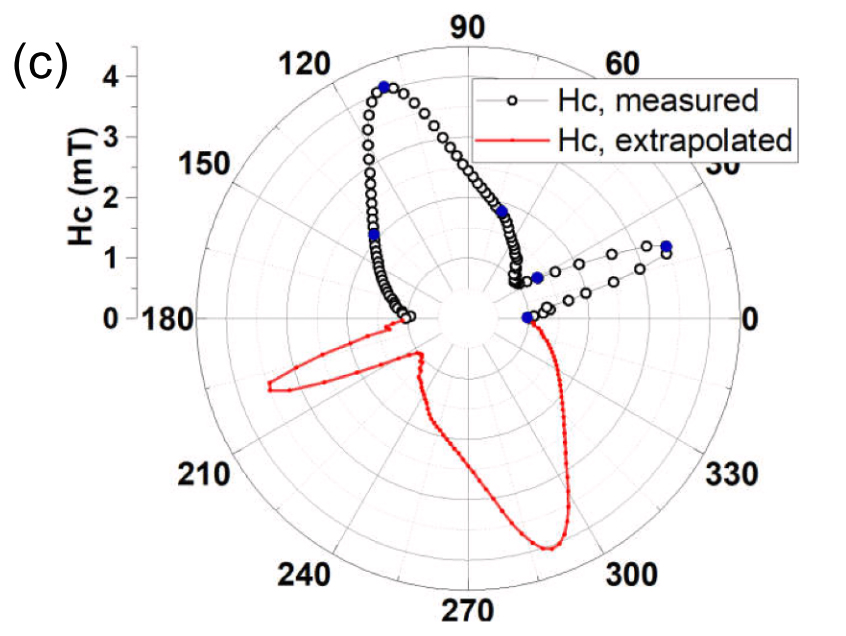
I.V. Soldatov, J. Zehner, K. Leistner, T. Kang, D. Karnaushenko and R. Schäfer, JMMM. 529, 167889 (2021)
Based on a multi-component Kerr imaging technique we have developed a fully automated procedure for the measurement of magnetisation reversal loops along arbitrary in-plane field directions for magnetic films with in-plane anisotropy that does not require any mechanical adjustment of the system.
.
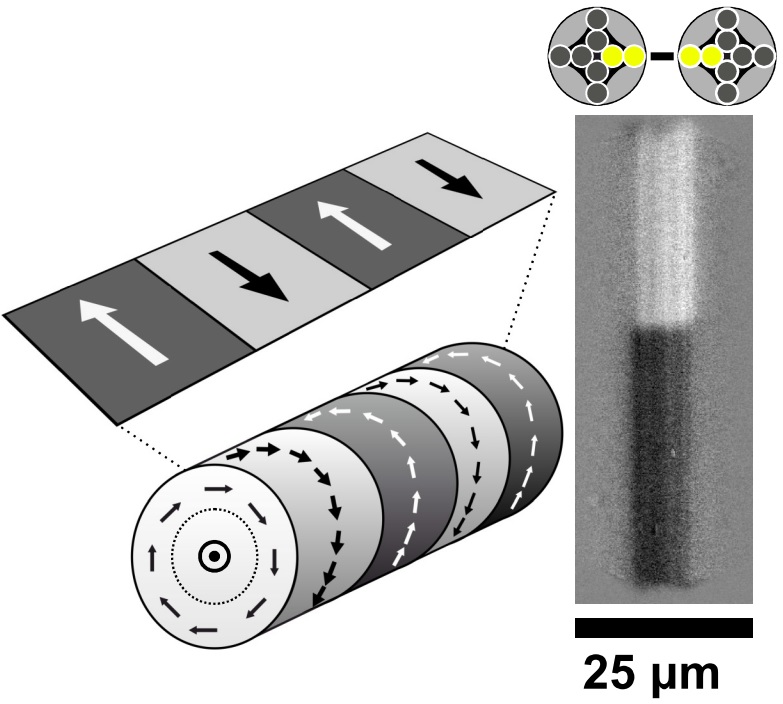
Interpretation of Kerr Microscopic Domain Contrast on Curved Surfaces
I.V. Soldatov, V. Kolesnikova, V. Rodionova and R. Schäfer, JMMM. 529, 167889 (2021)
In this letter, we address a technical peculiarity of wide-field magneto-optical Kerr microscopy, which may easily lead to a misinterpretation of the domain contrast on curved surfaces. On the example of circumferentially magnetized domains in ferromagnetic microwires, we show that the checkerboard domain pattern, which typically shows up in polar Kerr sensitivity, is caused by the superposition of longitudinal Kerr contrasts that arise from in-plane magnetization components and inclined light incidence rather than from the magnetization components perpendicular to the focal plane as claimed in the literature. Experimental ways to avoid such peculiar contrasts are demonstrated.
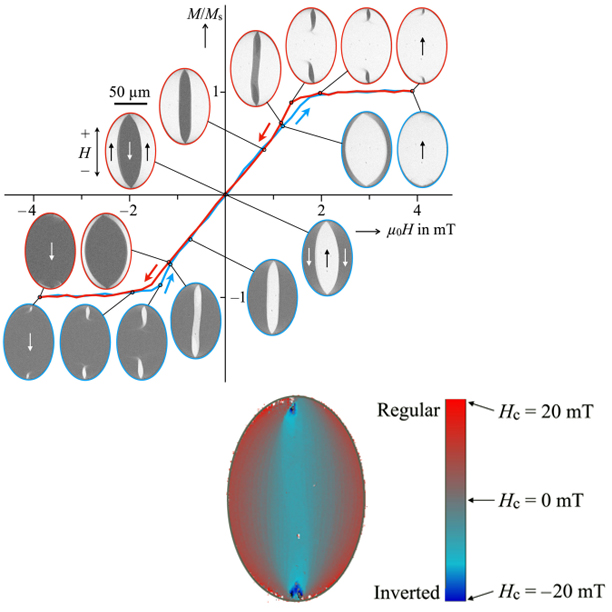
Inverted Hysteresis, Magnetic Domains, and Hysterons
I. Soldatov, P. Andrei, R. Schäfer, IEEE Magnetics Letters, 1, 2405805 (2020)
In this letter, we use magnetooptical Kerr effect magnetometry on extended samples to measure local hysteresis curves as a function of an externally applied field in a magnetostriction-free amorphous ribbon and an elliptical Permalloy film element. Although these materials are magnetically soft and have almost zero coercive field, we find that the local hysteresis curves have a highly nonlinear hysteretic character, displaying both counterclockwise and clockwise rotation senses when cycling the loops. This unexpected result can be explained by looking at the total hysteresis curve of the materials as a superposition of local curves and can be described mathematically using the formalism of the Preisach model. Within the framework of this model, we derive the conditions under which a superposition of clockwise and counterclockwise hysteresis loops can lead to a hysteresis-less system, and devise a technique to map the hysterons that define the first-order reversal-curve distribution to physical regions in the specimens.
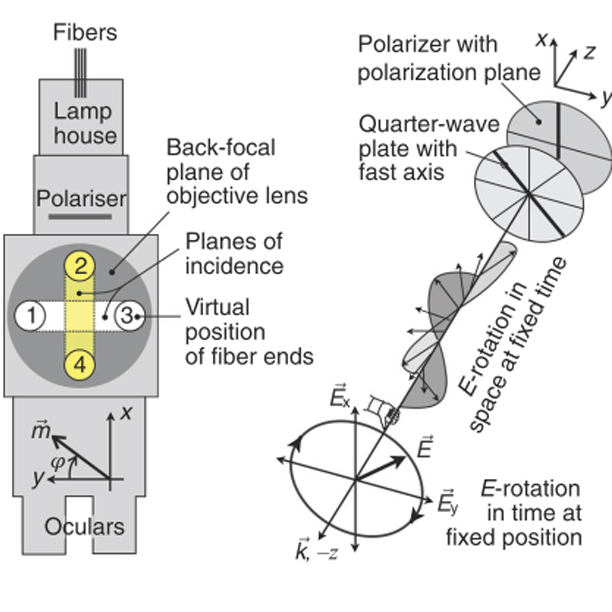
Analyzer-free, intensity-based, wide-field magneto-optical microscopy
R. Schäfer, P. M. Oppeneer, A. V. Ognev, A. S. Samardak, I. Soldatov, Applied Physics Review, 8 (3), 031402 (2021)
In conventional Kerr and Faraday microscopy, the sample is illuminated with plane-polarized light, and a magnetic domain contrast is generated by an analyzer making use of the Kerr or Faraday rotation. Here, we demonstrate possibilities of analyzer-free magneto-optical microscopy based on magnetization-dependent intensity modulations of the light. (i) The transverse Kerr effect can be applied for in-plane magnetized material, as demonstrated for an FeSi sheet. (ii) Illuminating that sample with circularly polarized light leads to a domain contrast with a different symmetry from the conventional Kerr contrast. (iii) Circular polarization can also be used for perpendicularly magnetized material, as demonstrated for garnet and ultrathin CoFeB films. (iv) Plane-polarized light at a specific angle can be employed for both in-plane and perpendicular media. (v) Perpendicular light incidence leads to a domain contrast on in-plane materials that is quadratic in the magnetization and to a domain boundary contrast. (vi) Domain contrast can even be obtained without a polarizer. In cases (ii) and (iii), the contrast is generated by magnetic circular dichroism (i.e., differential absorption of left- and right-circularly polarized light induced by magnetization components along the direction of light propagation), while magnetic linear dichroism (differential absorption of linearly polarized light induced by magnetization components transverse to propagation) is responsible for the contrast in case (v). The domain–boundary contrast is due to the magneto-optical gradient effect. A domain–boundary contrast can also arise by interference of phase-shifted magneto-optical amplitudes. An explanation of these contrast phenomena is provided in terms of Maxwell–Fresnel theory.
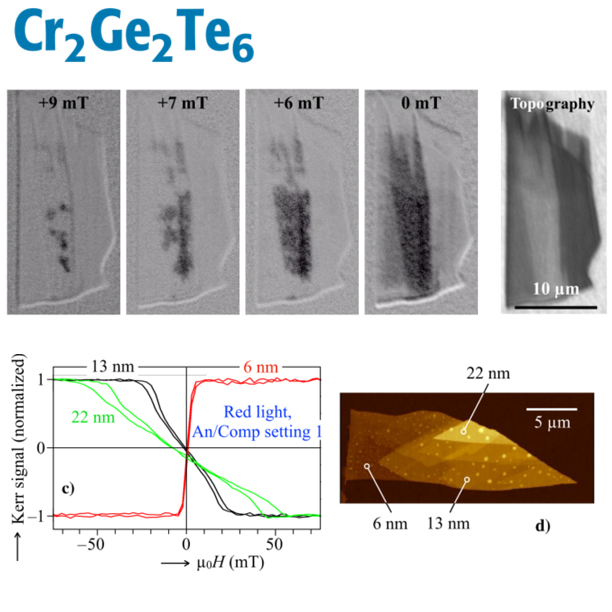
Wide-Field Kerr Microscopy and Magnetometry on Cr₂Ge₂Te₆ Exfoliated van-der-Waals Flakes
I. Soldatov, B. Özer, S. Aswartham, S. Selter, L. Veyrat, B. Büchner and R. Schäfer, IEEE Access, 12, 181025, (2024)
The potential of wide-field magneto-optical Kerr microscopy for the characterisation of low-dimensional van-der-Waals crystals is explored using the example of CrGeTe flakes in the ten nanometers thickness range. Although the magnetic domains with an expected width in the hundred-nanometer range cannot be seen on this material due to the limited lateral resolution, we show that Kerr microscopy is nevertheless a very valuable method for measuring the magnetization loops on selectable thickness regions on the flake. From the loop character one can indirectly infer on the existence or suppression of band domains, which are the equilibrium patterns above a film thickness of about 7nm. We derived this characteristic thickness from the initial susceptibility of the hysteresis loops and used it to estimate the specific domain wall energy to be 2.7⋅10^(−4) J/m2. We further demonstrate a thickness- and light colour dependent sign inversion of the Kerr signal that is explained by a Fresnel-type depth sensitivity concept. Accordingly, the Kerr contrast is governed by the relative phase of the Kerr amplitude that can be freely adjusted by a rotatable compensator. The compensator is thus the decisive optical element in magneto-optical Kerr magnetometry and microscopy on low-dimensional materials. It needs to be appropriately aligned to avoid a cancelation of the Kerr contrast and to maximise the Kerr signal.
