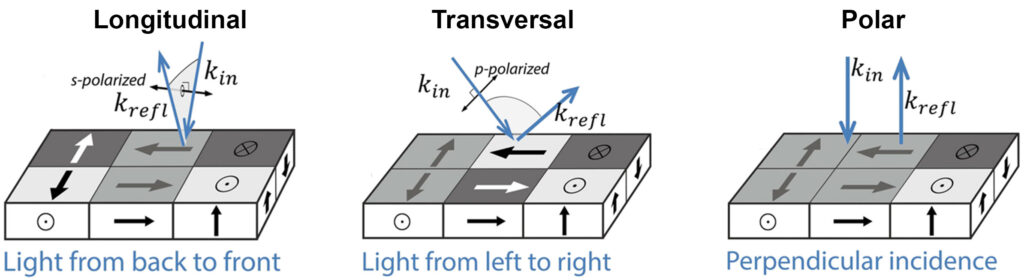
Sensitivity directions
The three spatial components of the magnetization vector of a sample can be defined along the microscope axis (called longitudinal here), transverse to the microscope axis (called transversal here) and perpendicular to the sample surface (called polar here).
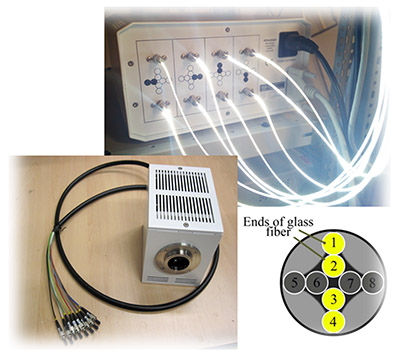
Advanced light source
evico magnetics has developed a light source, based on the 8 ultra-bright LEDs. Utilizing the novel setup all three components can be imaged separately under computer control. It is available in a monochromatic and an dichromatic configuration
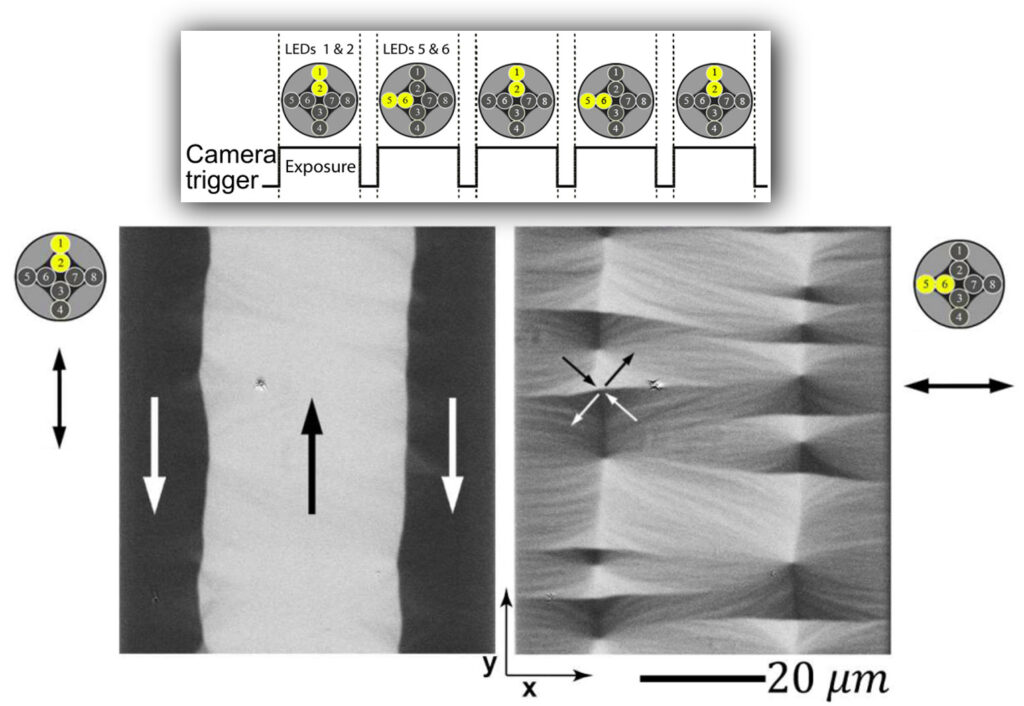
The monochromatic solution is based on LEDs of the same colour (white, red, blue and green LEDs are possible). Selected LEDs are either continuously activated or run in a pulsed mode synchronized with the camera to achieve the desired Kerr sensitivity. The following Kerr contrast options are possible: (i) longitudinal sensitivity with superimposed polar sensitivity, (ii) transverse sensitivity with superimposed polar sensitivity and (iii) pure polar sensitivity. In each case, a single domain image is displayed on the screen. (iv) simultaneous display of longitudinal and transverse contrast (with superimposed polar contrast) in two separate images on the screen, (v) display of pure longitudinal contrast in a single image, and (vi) display of pure transverse contrast in a single image on the screen.
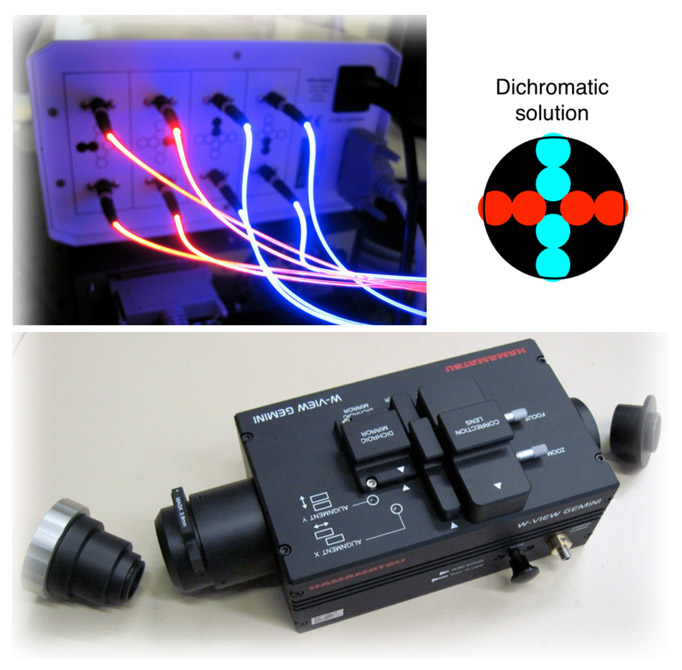

The dichromatic configuration is based on dichromatic imaging, where red and blue LEDs are used in a specific arrangement. Two images of different color and Kerr sensitivity are generated simultaneously, separated by a color-sensitive image splitting device between the microscope and camera. Both images are then displayed simultaneously in the same frame on the screen. With this advanced setup, the same sensitivity options can be achieved as with the standard configurations when the image splitter is used in bypass mode. By activating the image splitter, the following additional contrast options are available: (i) simultaneous display of longitudinal and transverse sensitivity, both with superimposed polar contrast, in the same frame, (ii) simultaneous display of pure longitudinal and pure transverse sensitivity in the same frame, (iii) simultaneous display of pure longitudinal and polar sensitivity in the same frame and (iv) simultaneous display of pure transverse and polar sensitivity in the same frame.
The contrast separation in the Kerr microscopy is further addressed in Relevant technical publications and in the following paper:
Selective sensitivity in Kerr microscopy (I. V. Soldatov and R. Schäfer, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88, 073701 (2017))
